Alongside hydropower, wind power and bioenergy, photovoltaics will play a key role in an energy scenario based on renewable energy sources. Assuming that, in the long term, the energy system will see large-scale electrification and all major industrial processes and the mobility system will switch to electricity, photovoltaics has the potential to meet some 15% of Austria’s electricity demand by 2030, rising to around 27% by 2050.* The space this will require is already available on existing roofs and facades. If this potential is to be leveraged, however, the power system will have to be made more flexible across the board.
*Source: Technology Roadmap for Photovoltaics in Austria, BMVIT 2016
The IEA is forecasting that solar energy will make up 27% of the global electricity supply mix in 2050. Its Photovoltaic Power Systems Programme (PVPS TCP) is the world’s biggest platform for photovoltaics research and has offered a space for applied research activities and market launch strategies for over 25 years. The focus during the 2018-2022 working period is on the role of photovoltaics (PV) in integrated energy systems. Key research topics include PV in buildings, PV in the transport sector and integrating a high percentage of PV power into grids. Austria is currently involved in seven of the eight ongoing tasks.
One of the areas that will become particularly prominent in future is building-integrated photovoltaics (BiPV), a technology being researched as part of IEA PVPS Task 15 under the leadership of Austria. PV facilities can be integrated into a building’s concept as active components and act as its roof membrane, facade and sunshade. Austria has extensive expertise in this area. Austrian industry has already completed a large number of projects all around the world in partnership with researchers and is one of the leading players in this field.
https://nachhaltigwirtschaften.at/de/iea/technologieprogramme/pvps/
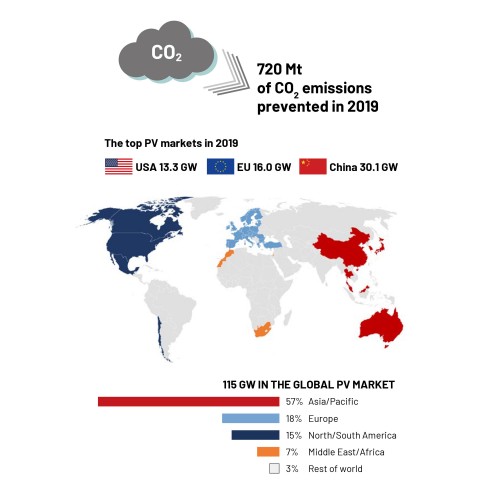
The IEA PVPS Snapshot Report 2020 provides an overview of the latest global trends on the photovoltaics market, in production and in the relevant framework conditions. After a year of stabilisation on the market, provisional market data indicate that the global PV market expanded somewhat in 2019 compared with 2018 and 2017. Across the world, 114.9 GW was installed and brought on stream last year. The total installed capacity for photovoltaics stood at 627 GW. China’s PV market shrank from 53.0 GW (2017) and 43.4 GW (2018) to 30.1 GW in 2019. In capacity terms, however, China remains out in front at 204.7 GW. The EU installed nearly 16 GW in 2019, with the rest of Europe adding some 5 GW. After years of a stagnating market, Spain led the field in the EU in 2019 with 4.4 GW, followed by Germany in second place with 3.9 GW and the Netherlands in third with 2.4 GW. With 224 MW, Austria came ninth out of the EU countries. https://iea-pvps.org/snapshot-reports/snapshot-2020/
https://iea-pvps.org/snapshot-reports/snapshot-2020/
![]()
Cover Power – Smart Glass Coatings for innovative BiPV Solutions
In the Cover Power project, which is being supported as part of SOLAR-ERAnet (project number: 863509), researchers at Joanneum Research Forschungsgesellschaft are developing innovative solutions for the surfaces of PV modules. How a photovoltaic solution looks largely depends on the glass used to cover the PV modules. Combining different types of coatings with different glass patterns is opening up new opportunities for designing innovative BiPV solutions.
Prototypes of BiPV modules are being developed that are based on glass-glass technology and c-Si solar cells (including bifacial cells) and feature innovative glass coatings on the outside of the cover glass. These module prototypes have the following properties:
> flexible, innovative design in terms of colour and surface structure
> minimum glare (less than 0.1% of mirror reflection)
> at least 150 W/m2 (STC) achieved by using internally reflected light inside bifacial solar cells
There are plans to install the solar modules on a pilot facade. The new module prototypes are set to be trialled and evaluated in the third year of the project.
www.solar-era.net/index.php/download_file/view/695/200/

